Seventeen people have been killed by lightning over the last two days in various parts of Bihar, Six deaths have been reported from Bhagalpur district, while three people were killed in Vaishali, and two each in Banka and Khagaria. Other deaths happened in Madhepura, Saharsa, Munger and Katihar.
Of all the atmospheric phenomena, lightning perhaps is the most dangerous and mysterious. In India, lightning kills about 2,000-2,500 people every year. Bihar is just one of the several hotspots for lightning in India, as a new atlas of lightning shows.
What is lightning?
Scientifically, lightning is a rapid and massive discharge of electricity in the atmosphere some of which is directed towards earth. The discharges are generated in giant moisture-bearing clouds that are 10-12 km tall. The base of these clouds typically lie within 1-2 km of the Earth’s surface, while the top is 12-13 km away. Temperatures in the top of these clouds are in the range of –35° to –45°C.
As water vapour moves upward in the cloud, the falling temperature causes it to condense. As they move to temperatures below 0°C, the water droplets change into small ice crystals. They continue to move up, gathering mass until they are so heavy that they start to fall to Earth. This leads to a system in which, simultaneously, smaller ice crystals are moving up and bigger crystals are coming down.
Collisions follow and trigger the release of electrons, a process that is very similar to the generation of sparks of electricity. As the moving free electrons cause more collisions and more electrons, a chain reaction ensues. This process results in a situation in which the top layer of the cloud gets positively charged, while the middle layer is negatively charged. The electrical potential difference between the two layers is huge, of the order of a billion to 10 billion volts. In very little time, a massive current, of the order of 100,000 to a million amperes, starts to flow between the layers.
While the Earth is a good conductor of electricity, it is electrically neutral. However, in comparison to the middle layer of the cloud, it becomes positively charged. As a result, about 15%-20% of the current gets directed towards the Earth as well. It is this flow of current that results in damage to life and property on Earth.
Direct lightning strikes are rare but even indirect strikes are fatal given the immense amount of charge involved.
Which areas are lightning-prone?
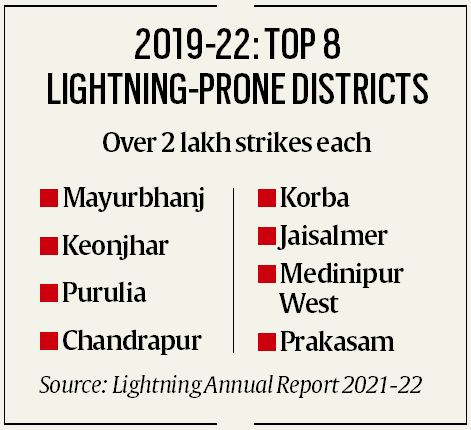
A recently released annual report on lightning by the Climate Resilient Observing Systems Promotion Council (CROPC), which works closely with government agencies like the India Meteorological Department, includes a lightning atlas which maps vulnerability at the district level.
According to the report, Madhya Pradesh has reported the largest number of cloud to ground lighting strikes, followed by Chhatisgarh, Maharashtra, Odisha and West Bengal. Other states with high strike rate include Bihar, UP, Karnataka, Jharkhand and Tamil Nadu.
Lightning is fairly common, though it is not often realised in the urban centres. In India, well over one crore lightning strikes have been recorded in recent years. It is only over the last few years that lightning records have begun to be maintained, thanks to the efforts of CROPC and India Meteorological Department.
In 2019-20, about 1.4 crore lightning strikes were recorded, which increased to 1.85 crore in 2020-21.
In 2021-22, about 1.49 crore strikes were recorded across the country. The reduction, in line with the trend observed globally, has been attributed to the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic.
“The reason attributed to reduction in lightning is due to Covid-2019 pandemic induced reduction in aerosol level, pollution, environmental upgradation and relatively stable weather system in Indian subcontinent,” the annual lightning report said.
But most of this reduction was seen in the cloud-to-cloud lightning. Of the strikes that reach the Earth, only a 2.5% reduction was observed.
How can the effects of lightning strikes be mitigated?
Lightning is not classified as a natural disaster in India. But recent efforts have resulted in the setting up of an early warning system, that is already saving many lives. More than 96% of lightning deaths happen in rural areas. As such, most of the mitigation and public awareness programmes need to focus on these communities.
Lightning protection devices are fairly unsophisticated and low-cost. Yet, their deployment in the rural areas, as of now, is extremely low.
States are being encouraged to prepare and implement lightning action plans, on the lines of heat action plans. An international centre for excellence on lightning research to boost detection and early warning systems is also in the process of being set up.
Written by Parthasarathi Biswas , Amitabh Sinha
Source: Indian Express, 21/06/22